rueki
6. Pytorch를 이용한 MNIST 이미지 ANN Classification 본문
이번에는 ANN을 이용해서 MNIST 이미지를 분류해보는 모델을 만들어보자.
파이토치에는 비젼분야를 위한 torchvision이 있어서 매우 용이하다.
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
import numpy as np
import pandas as np
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline앞서 작성한 글에서도 언급했듯이, 어떤 데이터가 되었든 간에 모델 학습을 위해서 데이터 형태는 텐서로 구성이 되어 있어야하며, 이미지 역시 마찬가지이다.
여기서 이미지를 텐서로 바꾸어주는 transforms를 사용할 것이다.
transform = transforms.ToTensor()이 코드로 인해서 image to Tensor 가 가능하다.
이제 MNIST 데이터를 불러올 것인데 이는 파이토치의 내부 데이터 셋에 있다.
train_data = datasets.MNIST(root='../data', train=True, download=True, transform=transform)
test_data = datasets.MNIST(root='../data',train=False, download=True, transform=transform)MNIST 데이터를 train set과 Test set으로 구분해서 불러왔으며, train_data 에는 60000장, test_data에는 10000장이 있다.
train_data[0]
'''
(tensor([[[0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000,
0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000,
0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000,
0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000],
[0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000,
0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000,
.
.
.
[0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000,
0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000,
0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000,
0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000],
[0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000,
0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000,
0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000,
0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000]]]), 5)
'''train_data를 봤을 때 , 이미지 텐서 값과 마지막에 레이블 값으로 구성된 것을 확인할 수 있다.
image, label = train_data[0]
image.shape
# torch.Size([1, 28, 28])
label # 5이미지는 (1,28,28) 의 형태를 갖고 있는데, 이는 28 x 28 이미지에 Grey color channel을 갖고 있다는 뜻이다.
plt.imshow(image.reshape(28,28),cmap='gist_yarg')
시각화를 통해서 5의 이미지를 확인해보았다.
데이터가 적은 경우는 상관 없지만, 데이터가 많은 경우에는 연산 속도가 오래걸리기에 데이터를 나누어서 계산을 하는 미니 배치를 적용한다. 파이토치에서는 DataLoader를 통해 batch_size를 정할 수 있다.
torch.manual_seed(101)
# 0 images, 1 images....
train_loader = DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=100, shuffle=True)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_data,batch_size=500, shuffle=False)from torchvision.utils import make_grid
np.set_printoptions(formatter=dict(int=lambda x : f'{x:4}')) #formatting
#first batch
for images,labels in train_loader:
break
images.shape
# torch.Size([100, 1, 28, 28])
# 100개 이미지, 28 x 28 그레이 스케일
labels.shape
# torch.Size([100])
print('Labels:', labels[:12].numpy())
im = make_grid(images[:12],nrow=12)
plt.figure(figsize=(10,4))
plt.imshow(np.transpose(im.numpy(),(1,2,0))) # color, width, height -> whcLabels: [ 0 5 7 8 6 7 9 7 1 3 8 4]
Out[33]:
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x23b3ee37cc8>

100개의 이미지 중에서 12개의 이미지와 레이블 값을 확인해보았다.
이제 모델을 만들어보자.
class MultilayerPerceptron(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_sz , out_sz, layers=[120, 84]):
super().__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(in_sz,layers[0])
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(layers[0],layers[1])
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(layers[1],out_sz)
def forward(self, X):
X = F.relu(self.fc1(X))
X = F.relu(self.fc2(X))
X = self.fc3(X)
return F.log_softmax(X,dim = 1)위와 같이 fully connected layer를 3개를 만들었다. input ->hidden -> hidden -> output
입력으로는 28 x 28 = 784개를 입력해서 첫번째 은닉층으로 120, 두번째는 84, 출력으로는 0 ~ 9 의 10개로 신경망 모델을 구성하였으며, 순전파에는 전부 relu 함수를 사용하였다.
return 값으로는 이번에 다루는 문제가 multiclass classification 이므로 softmax를 사용하였다.
torch.manual_seed(101)
model = MultilayerPerceptron()
model
'''
:
MultilayerPerceptron(
(fc1): Linear(in_features=784, out_features=120, bias=True)
(fc2): Linear(in_features=120, out_features=84, bias=True)
(fc3): Linear(in_features=84, out_features=10, bias=True)
)
'''모델을 생성했으니 이제 손실함수와 최적화 함수를 구현하자.
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(),lr=0.001)모델을 훈련해보자.
import time
start_time = time.time()
#training
epochs = 10
train_losses = []
test_losses = []
train_correct = []
test_correct = []
for i in range(epochs):
trn_corr = 0
tst_corr = 0
for b,(X_train, y_train) in enumerate(train_loader): #image / label
b += 1 #index 값
y_pred = model(X_train.view(100,-1))
loss = criterion(y_pred, y_train)
predicted = torch.max(y_pred.data, 1)[1]
batch_corr = (predicted == y_train).sum()
trn_corr += batch_corr
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if b%200==0:
acc = trn_corr.item() * 100 / (100*b)
print(f'epoch {i} batch {b} loss : {loss.item()} acc : {acc}')
train_losses.append(loss)
train_correct.append(trn_corr)모델을 훈련하고 이제 테스트 데이터에 대해서 성능 평가를 해야한다.
with torch.no_grad():
for b, (X_test, y_test) in enumerate(test_loader):
y_val = model(X_test.view(500,-1))
predicted = torch.max(y_val.data,1)[1]
tst_corr += (predicted== y_test).sum()
loss = criterion(y_val,y_test)
test_losses.append(loss)
test_correct.append(tst_corr)
total_time = time.time() - start_time
print(f'Duration : {total_time/60}mins')여기서 with 문은 위의 첫 번째 for문 안에 같이 선언해줘야한다.
plt.plot(train_losses,label='Training Loss')
plt.plot(test_losses, label='test/validation loss')
plt.legend()
train data와 test data의 loss를 비교해보니 꽤 차이가 나는 것을 볼 수가 있다.
train_acc = [t/600 for t in train_correct]
test_acc = [t/100 for t in test_correct]
plt.plot(train_acc,label='train acc')
plt.plot(test_acc , label='test acc')
plt.legend()
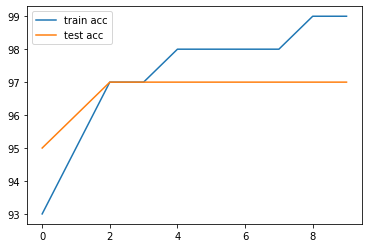
이번 시간에는 ANN을 구현해서 MNIST 이미지 파일을 Multi-Classification을 해보았다.
CNN으로는 어떻게 구현하는지 다음에 알아보도록 하겠다.
'pytorch' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Simple RNN 구현 (3) | 2020.03.31 |
|---|---|
| 7. Pytorch를 이용한 MNIST CNN 구현 (0) | 2020.03.24 |
| 6. Pytorch를 이용한 ANN 구현 (0) | 2020.03.07 |
| 5. pytorch를 이용한 Linear Regression (0) | 2020.03.07 |
| 4. Gradient Descent (0) | 2020.03.05 |




